DNS and ARP
14 Jun 2022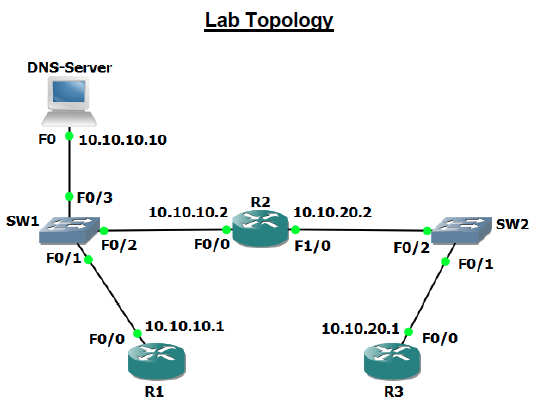
In this lab:
- Configure Cisco routers to use DNS
- Examine router ARP caches
Configure Cisco routers to use DNS
The Domain Name System (DNS) protocol is used to translates domain names into their corresponding IP addresses. DNS uses port 53 and typically DNS records are stored on a DNS server either locally or externally. In this lab we will be configuring our routers to use the local DNS server at 10.10.10.10
On each router I will use the commands;
ip domain-lookupip name-server 10.10.10.10
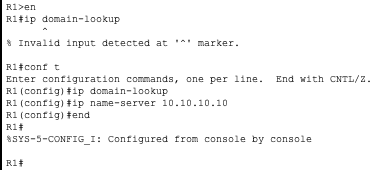
R1
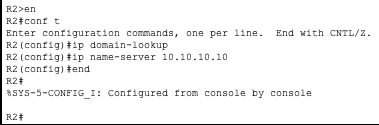
R2
R3
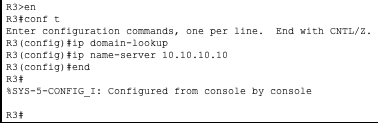
Now that we have all the routers configured to use 10.10.10.10 as their name server we can communicate with them using their hostnames instead of IP’s.
R1
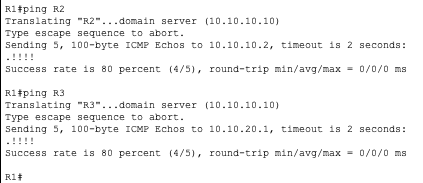
Note:
Cisco routers can also be configured to act as DNS servers using the commands;
ip dns serverip host <hostname> <ip>
Examine router ARP caches
Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) exists to identify layer 2 addresses with a devices physical interface. ARP is broadcast traffic which also means routers do not forward any ARP requests to the rest of the network. Because of this, as you’ll see below, each router will have a slightly different ARP cache.
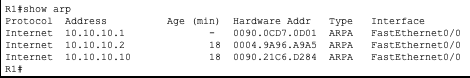
R1
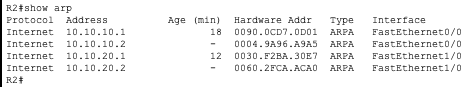
R2
R3
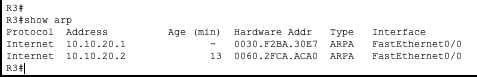
As you can see in the ARP tables R1 only has entries for the 10.10.10.0/24 network and R3 only has entries for the 10.10.20.0/24 network. This is because they are separated by R2 which does not forward ARP requests.
This is the same reason R2 has entries for both networks.