Cisco IOS Basics
14 May 2022In this lab:
- User Exec Mode
- Privileged Exec Mode
- Global Config Mode
- IOS Configuration Management
User Exec Mode:
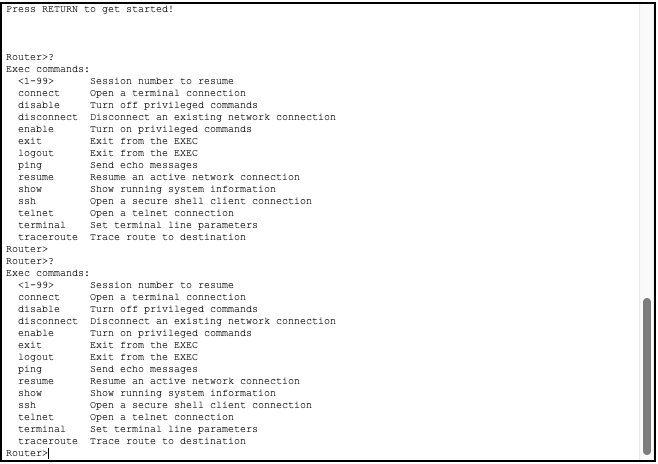
User exec mode is denoted by the ‘>’ character when using the command line.
This mode gives users access to basic commands that can be seen with the ? command.
In order to access additional commands you must elevate your privilege to additional modes.
Privileged Exec Mode:
Privileged exec mode is denoted by ‘#’ character when using the command line.
Privileged exec mode is entered by using the enable command at user exec mode. You can also downgrade privileges by using disable command.

Cisco IOS supports shortened commands, allowing us to use en as the same command as enable. Cisco IOS will infer the command when the characters can possibly only match on command. In order to view all possible matches use the ‘?’ character at the end of your command.

Using the ‘?’ character after using a space will show additional parameters for that command.
When a command gives you more output then the screen can hold, you can cycle through by using the enter key to scroll one line at a time or the space key to scroll one page at a time.
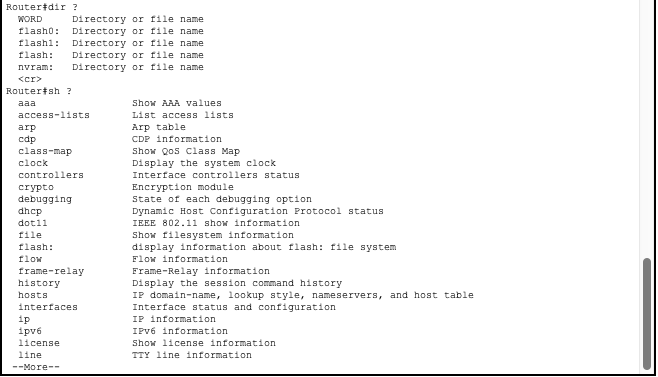
Cisco IOS supports tab auto-completion.
Global Config Mode:
Global configuration mode is denoted by the ‘config’ characters when using the command line.
Here you can enter configuration commands that affect the device as a whole.
All valid commands entered in global config mode will be stored in the devices ‘running-config’. This file is viewed by using the command show running-config however surprisingly cannot be run from global config mode. This is a command only valid in privileged exec mode. In order to run a command from privileged exec mode (this works at any modes beside global config as well) we use the do keyword.
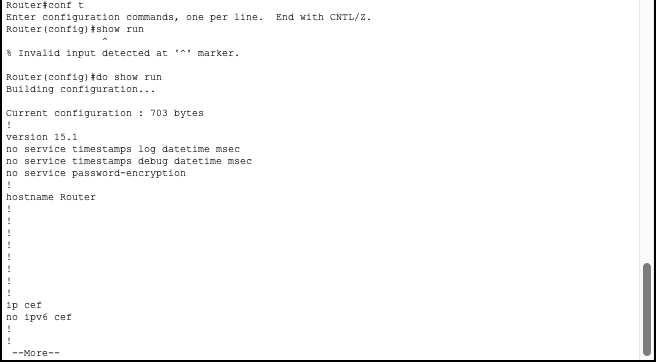
Cisco IOS supports piping commands, which is useful when crawling through logs. Some useful commands are;
do show run | begin hostname: Shows the running config, starting from first occurrence of ‘hostname’do show run | include interface: Shows only the lines including ‘interface’do show run | exclude interface: Shows only lines not including ‘interface’
Global config mode also allows us to enter interface configuration mode for the device interfaces. From there we can enter commands specifically for that interface.
To leave interface configuration mode use the exit command.
To downgrade to privileged exec mode use the end command.

IOS Configuration Management:
It is common practice to give the device a hostname in order to more easily keep track of devices. Here we will name this device ‘Router1’ using the hostname <hostname command.
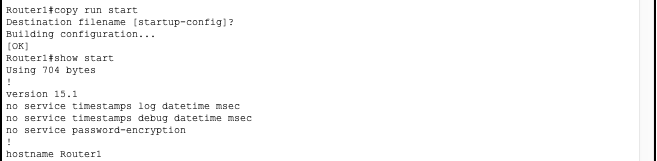
Here we see that our hostname was saved to the startup config and will now be persistent after a reboot.
Two other important commands are;
copy run flash: Copies the running config to flash memorycopy run tftp: Copies running config to external tftp server